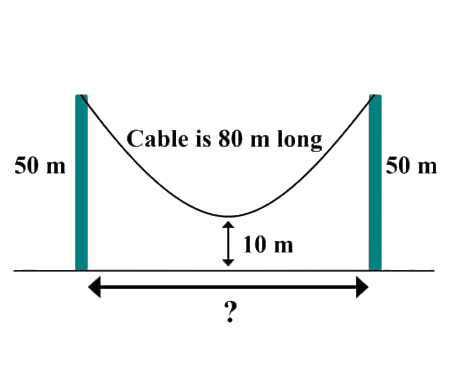
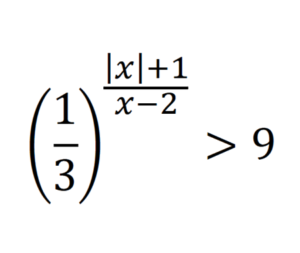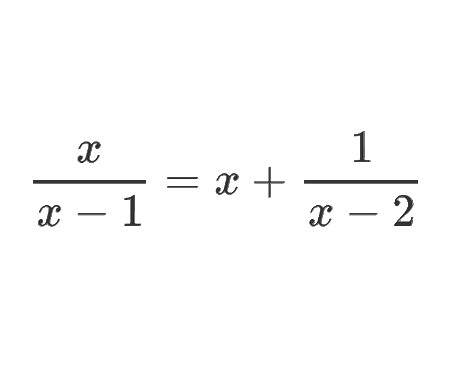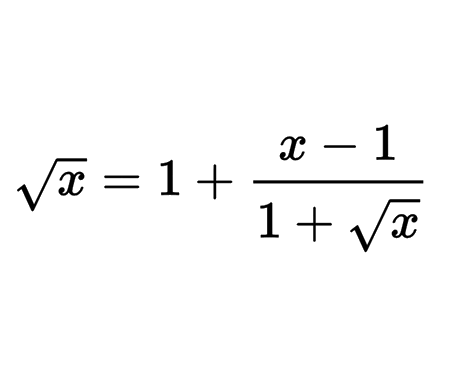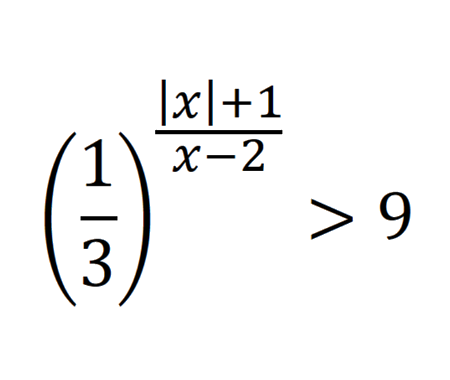Home -> Solved problems -> Inequalities
Mathematics: Inequalities
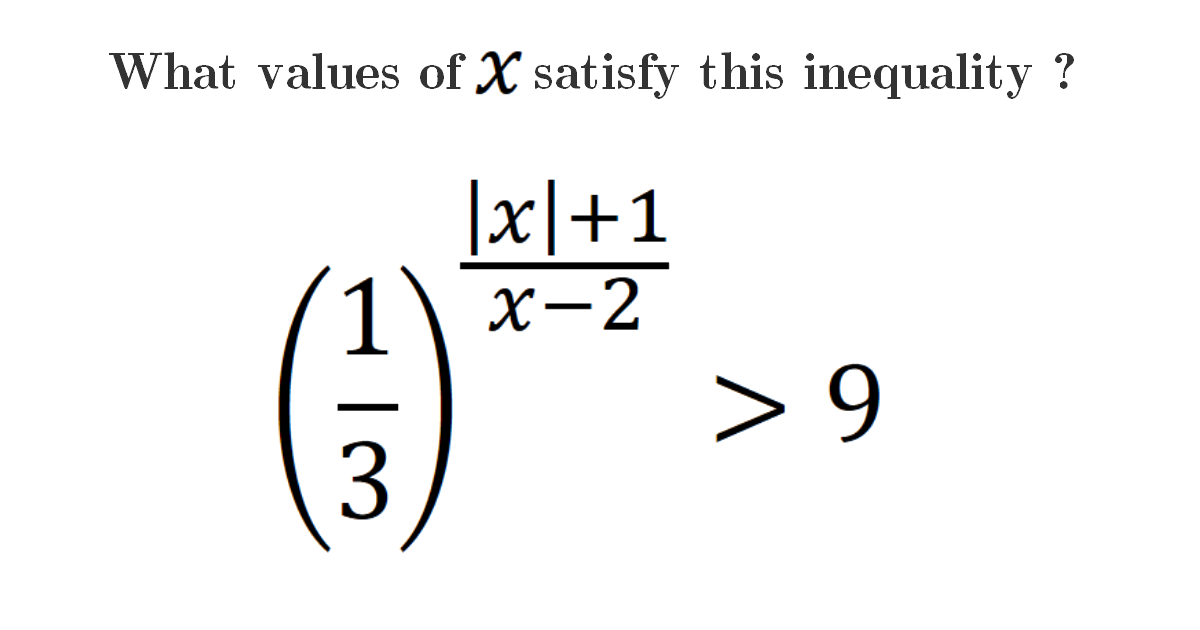
Solution
\[\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^{\frac{|x|+1}{x-2}}>9\] \[\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^{\frac{|x|+1}{x-2}}>\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^{-2}\] The expression exists when, \[\frac{|x|+1}{x-2}<-2\] Now, we focus on the absolute value of \(x\) \[\] If \(x<0\) \[\frac{-x+1+2 x-4}{x-2}<0\] \[\frac{x-3}{x-2}<0\] \[\frac{(x-3)(x-2)}{(x-2)^{2}}<0\] \[\Rightarrow 2<x<3\] We have a contradiction for this case. \[\] If \(x\geq0\) \[\frac{x+1+2 x-4}{x-2}<0\] \[\frac{3x-3}{x-2}<0\] \[\frac{(3x-3)(x-2)}{(x-2)^{2}}<0\] \[\frac{3(x-1)(x-2)}{(x-2)^{2}}<0\] \[\Rightarrow 1<x<2\] For this case we have solutions. \[\] Finally, \[\huge S_{\mathbb{R}}=[0,+\infty[\cap] 1,2[=] 1,2[\]
Home -> Solved problems -> Inequalities
Related Topics
Home -> Solved problems -> Inequalities
Share the solution: Inequalities